TICKETS, MONEY, PASSPORT!
REFLEXIVE PRONOUNS

We often use reflexive pronouns when the subject and the object of the verb refer to the same person or thing:
He cut himself on the broken glass.
She made herself a cup of tea and sat down in front of the television.
Parents often blame themselves for the way their children behave.
We use a reflexive pronoun to make it clear who or what is being referred to.
We can use reflexive pronouns for emphasis:
The director of the company wrote to us himself to apologise for the dreadful service. (or The director of the company himself wrote to us to apologise for the dreadful service.)
We don’t use reflexive pronouns on their own as the subject of a clause, but we can use them with a noun or pronoun to emphasise the subject:
Parents and teachers always pass on to children what they themselveshave been told, and this has been going on for hundreds, or even thousands of years.
We often use reflexive pronouns with byto mean ‘alone’ or ‘without any help’:
The children made the entire meal by themselves.Why don’t you go by yourself?
EXERCISES
- Robert made this T-shirt .
- Lisa did her homework
- We helped to some Coke at the party.
- Emma, did you take the photo by ?
- I wrote this poem .
- He cut with the knife while he was doing the dishes.
- The lion can defend .
- My mother often talks to .
- Tim and Gerry, if you want more milk, help .
- Alice and Doris collected the stickers .
MODALS OF PERMISSION, REQUEST AND OFFER
The modal verbs are can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will and would.
The modals are used to show that we believe something is certain, probable or possible:
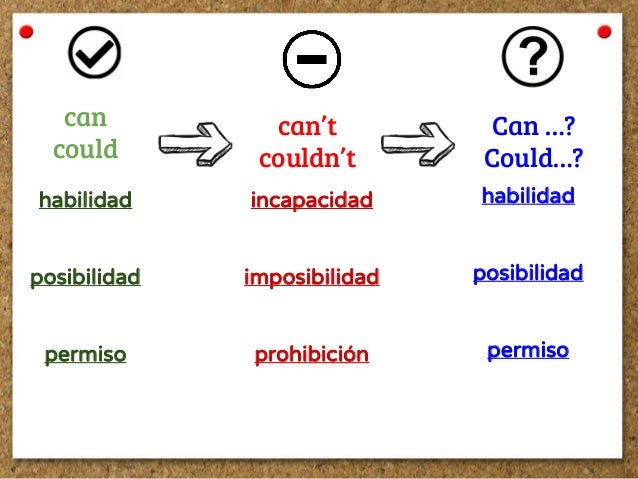

Possibility:
We use the modals could, might and may to show that something is possible in the future, but not certain:
They might come later. (= Perhaps/Maybe they will come later.)
They may come by car. (= Perhaps/Maybe they will come by car.)
If we don’t hurry we could be late. (= Perhaps/Maybe we will be late)
They may come by car. (= Perhaps/Maybe they will come by car.)
If we don’t hurry we could be late. (= Perhaps/Maybe we will be late)
We use could have, might have and may have to show that something was possible now or at some time in the past:
It’s ten o’clock. They might have arrived now.
They could have arrived hours ago.
They could have arrived hours ago.
We use the modal can to make general statements about what is possible:
It can be very cold in winter. (= It is sometimes very cold in winter)
You can easily lose your way in the dark. (= People often lose their way in the dark)
You can easily lose your way in the dark. (= People often lose their way in the dark)
We use the modal could as the past tense of can:
It could be very cold in winter. (= Sometimes it was very cold in winter.)
You could lose your way in the dark. (= People often lost their way in the dark)
You could lose your way in the dark. (= People often lost their way in the dark)
Impossibility:
We use the negative can’t or cannot to show that something is impossible:
That can’t be true.
You cannot be serious.
You cannot be serious.
We use couldn’t/could not to talk about the past:
We knew it could not be true.
He was obviously joking. He could not be serious.
He was obviously joking. He could not be serious.
Probability:
We use the modal should to suggest that something is true or will be true in the future, and to show you have reasons for your suggestion:
Ask Miranda. She should know.
It's nearly six o'clock. They should arrive soon.
It's nearly six o'clock. They should arrive soon.
We use should have to talk about the past:
It's nearly eleven o'clock. They should have arrived by now.

EXERCISES


Comentarios
Publicar un comentario